Html Tag:
HTML TAG is a tag used to identify an HTML document. The HTML html> element represents the root of an HTML document (or HTMLroot element). All other elements must inherit from this element. Aside from comments, the html>element is the root element because it is the first in a document. In HTML, this tag can be implied or omitted; in XHTML, however, it must be opened and closed.

HEAD TAG:
The initial element in an HTML page. TheDocument's metadata collection. The HTML head> element offers generic document information (metadata), such as its title and links to its scripts and style sheets.

Link Tag:
Other resources associated with the document. The link> element in HTML specifies the relationship between the current document and an external resource. This element may be used to define a relationship framework for navigation. Typically, this Element is used to link to style sheets.

TITLE TAG
Document title or name. The HTML element deတnes the titleof the document, shown in a browser's title bar or on the page's tab.It can only contain text, and any contained tags are ignored.

Address
The HTML address> element provides contact information for its closest ancestor article> or body>; in the latter instance, it applies to the entire text.

Article
A portion of the page's content, such as a blog entry or forum thread. The HTMLarticle> element denotes a self-contained composition designed to be independently distributable or reused inside a document, page, application, or website (e.g., in syndication). This might be a forum post, a magazine or newspaper article, a blog entry, an artefact, or any other piece of content that stands alone. Each article> element must have a heading (h1>-h6>) as a child.

H1 TO H6 TAG
The current section's heading. Heading elements implement six levels of document headers, with h1> being the most essential and h6> being the least. A heading element eloquently explains the subject of the section it begins. User agents may use heading information to automatically generate a document's table of contents, for instance.

Header
Elements of navigation or introduction for the current segment. The HTML header> element represents a group of navigational or introductory aids. It may contain heading components as well as other elements such as a logo, section header, search form, etc.

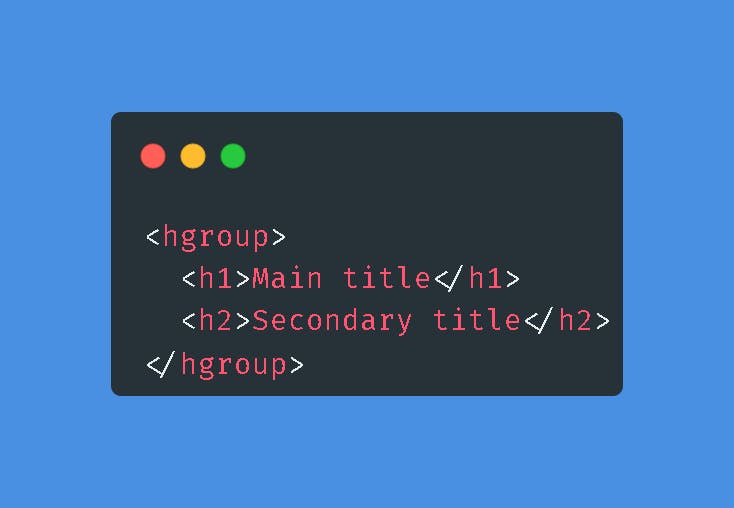
HGroup tag
The HTML Headings Group Element (hgroup>) represents the heading of a section. It identifies a single title that appears in the document's outline as the heading of the implicit or explicit section to which it belongs. Its text for the outline algorithm is the text of the rst HTML Heading Element with the highest rank (i.e., the rst h1>, h2>, h3>, h4>, h5>, or h6> with the fewest number among its children), and its rank is the rank of the HTML Heading Element itself. Therefore, this element unites multiple heads, contributing just the principal one to the document's outline. It permits associating auxiliary names, such as subheadings, alternative titles, or even slogans, with the document's primary heading without contaminating the document's structure.
Nav
A portion of a web page that contains links to other web pages. The HTML nav>element (HTML Navigation Element) denotes a segment of a page that contains links to other pages or sections within the same page: a segment containing navigation links.

This concludes the blog. This blog will teach you the most common HTML tags through the use of examples, which will assist you in structuring HTML documents. If you like it, please share it with your friends and we will see you in future articles.
